Cast & Sintered Alnico Magnets
group nameAlnico Magnets
-
Min Order1 piece
brand nameCINFER Magnet
payment methodT/T, L/C
-
update timeThu, 06 Dec 2018 13:35:03 GMT
Paramtents
Material Cast AlNiCo ,Sintered AlNiCo
Shape Any shape Can be customized
Coating Ni, Ni-Cu-Ni, Electroless Nickel, Zinc, Colored Zinc, Epoxy
Magnetized direction Axially or Diametrical Magnetized, but Thickness, Multipoles and Radial magnetization are also available
Certificate ISO/TS 16949, ISO9001, ISO14001, RoHS, REACH
Packing Standard sea or air packing, such as carton, wooden box, pallet etc.
Packging & Delivery
Min Order1 piece
Briefing
Detailed
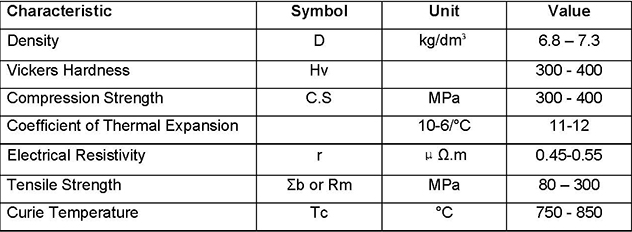
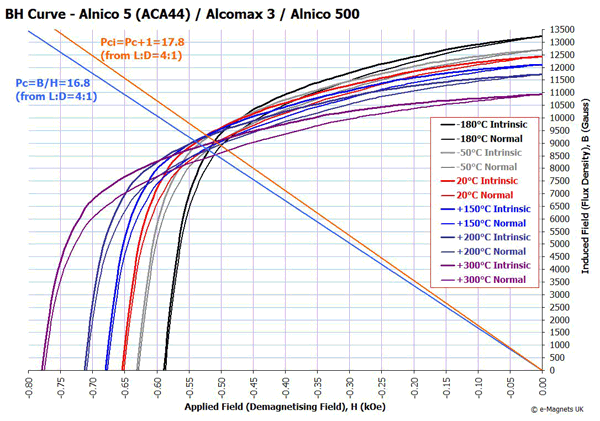
Alnico is an acronym referring to a family of iron alloys which in addition to iron are composed primarily of aluminium (Al), nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co), hence al-ni-co. They also include copper, and sometimes titanium. Alnico alloys are ferromagnetic, with a high coercivity (resistance to loss of magnetism) and are used to make permanent magnets. Before the development of rare earth magnets in the 1970s, they were the strongest type of magnet. Other trade names for alloys in this family are: Alni, Alcomax, Hycomax, Columax, and Ticonal.
The composition of alnico alloys is typically 8–12% Al, 15–26% Ni, 5–24% Co, up to 6% Cu, up to 1% Ti, and the balance is Fe. The development of alnico began in 1931, when T. Mishima in Japan discovered that an alloy of iron, nickel, and aluminum had a coercivity of 400 oersted (Oe; 32 kA/m), double that of the best magnet steels of the time.
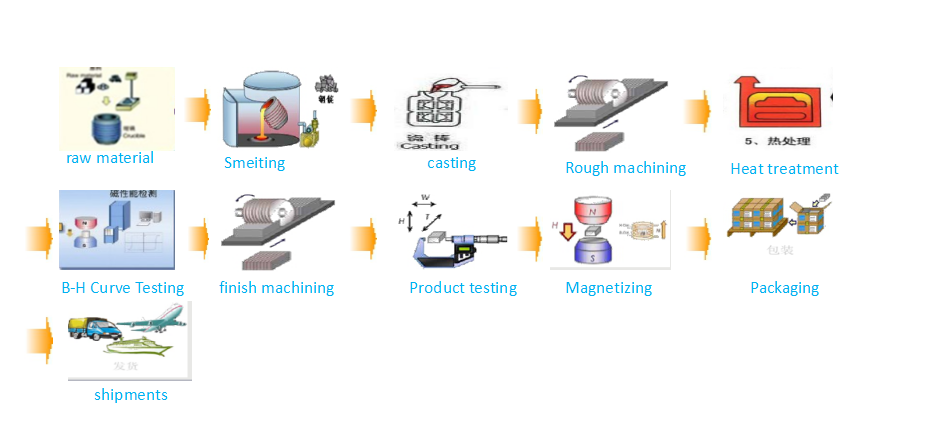
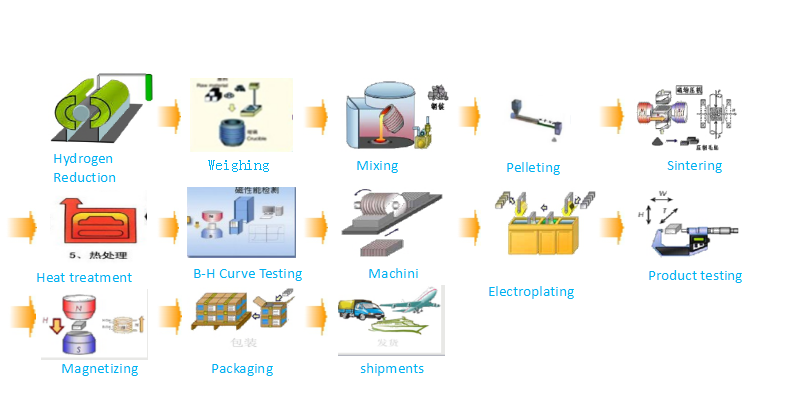
AlNiCo can be divided to cast AlNiCo and sintered AlNiCo. When compared with cast AlNiCo, sintered AlNiCo perform with lower magnetic properties but better mechanical properties. AlNiCo are brittle and hard, not suitable for traditional maching processes except grinding processing.
You need a product
You May Like
- Nearest port for product export
- Shanghai, Ningbo
- Delivery clauses under the trade mode
- FOB, CFR, CIF
- Acceptable payment methods
- T/T, L/C